Software Development Life Cycle
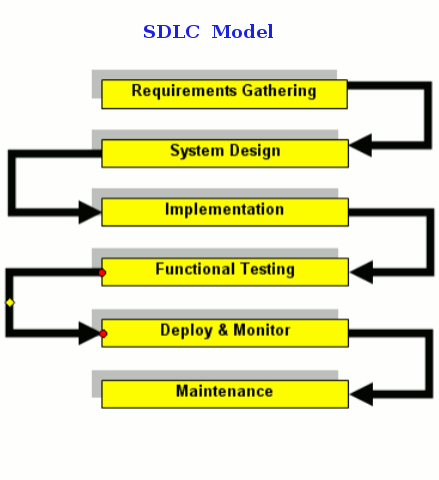
SDLC also known as Classic Life Cycle Model (or) Linear Sequential Model (or) Waterfall Method. This model has the following
activities.
1. System/Information Engineering and Modeling
Software is a large sysytem & work begins by the requirements for all system elements. System view is essential & software must interafce with other elements like hardware, people & resources.The development team studies the software requirement for the system
2. Software Requirement Analysis
This process is the feasibility study.The development team visit the client & studies the system. Team furnishes document at the end
of feasibility study which include costs, project schedule,target date etc.
3. System Analysis and Design
S/w overall structure is defined in this phase.The number of tier needed for package architecture, database design, data structure
design etc. The logical system of the product is developed in this phase.
4. Code Generation
The design must be translated into a machine readable form. Programming tool like compilers, interpreters, debuggers are used to
generate the code.
5. Testing
once code is generated the testing begins. Different testing methodologies are available to find the bugs.
6. Maintenance
S/w will definitely undergo changes once delivered to customers. changes can happen because of unexpected input values to the system.
Software should be developed to accomodate changes that could happen during post implementation period.
Prototyping Model
This is a cyclic version of the linear model. In this model, once the requirement analysis is done and the design for a prototype is made, the development process gets started. Once the prototype is created, it is given to the customer for evaluation.
Rapid Application Development (RAD) Model
The RAD model is a linear sequential software development process that emphasizes an extremely short development cycle. The RAD model is a "high speed" adaptation of the linear sequential model in which rapid development is achieved by using a component-based construction approach.
1. Business modeling
The information flow among business functions is modeled in a way that answers the following questions: What information drives the business process?What information is generated?
Who generates it?
Where does the information go?
Who processes it?
